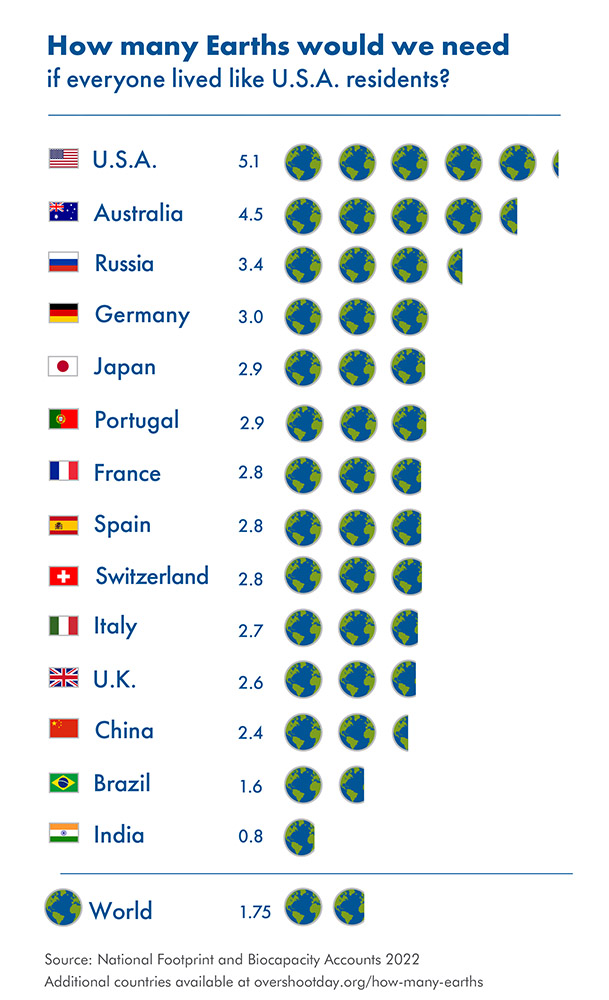
Zurich, May 10, 2023 – This year, Swiss Overshoot Day falls on May 13th. By then humanity would have used up as much as our planet’s ecosystems can renew in the entire year, if all people consumed at the rate of Swiss residents. It would take the regenerative capacity of nearly 3 Earths to provide that much. To mark that date, highlight possibilities, and warn Switzerland, FiBL, Gottlieb Duttweiler Institut, Soil to Soul, #MoveTheDate Switzerland, Swiss Food Research, and Global Footprint Network join forces.
Persistent overshoot has locked us into a future shaped by increasing climate change and resource constraints. This is true in every imaginable scenario. Also, these conditions are approaching faster than our cities, companies, energy infrastructure, and food systems can adjust. There is no benefit in reacting slowly.
Yet, there are many innovative initiatives in Switzerland that address overshoot. For example:
- Fabas and Vegional are food start-ups using legumes to produce nutritious food;
- Green Mountain has developed tasty plant-based meat alternatives;
- IT company SCS has retrofitted older machines to give them a longer life;
- Construction company Eberhard has pioneered construction waste recycling enabling circularity in the building industry;
- Carvolution reduces the need to own cars;
- Phenogy is developing batteries with zinc rather than rare lithium;
- Foodwaste.ch cuts just that, Madame Frigo, offers public fridges to share left-overs, Äss-Bar gives yesterday’s baking goods a second life;
- Umami and Yasai produce nutritious micro-greens in indoor water tanks imitating natural cycles.
- Vuna Nexus turns human urine into garden fertilizers;
- Cowa invented heat storage to upgrade the efficiency of heat-pumps.
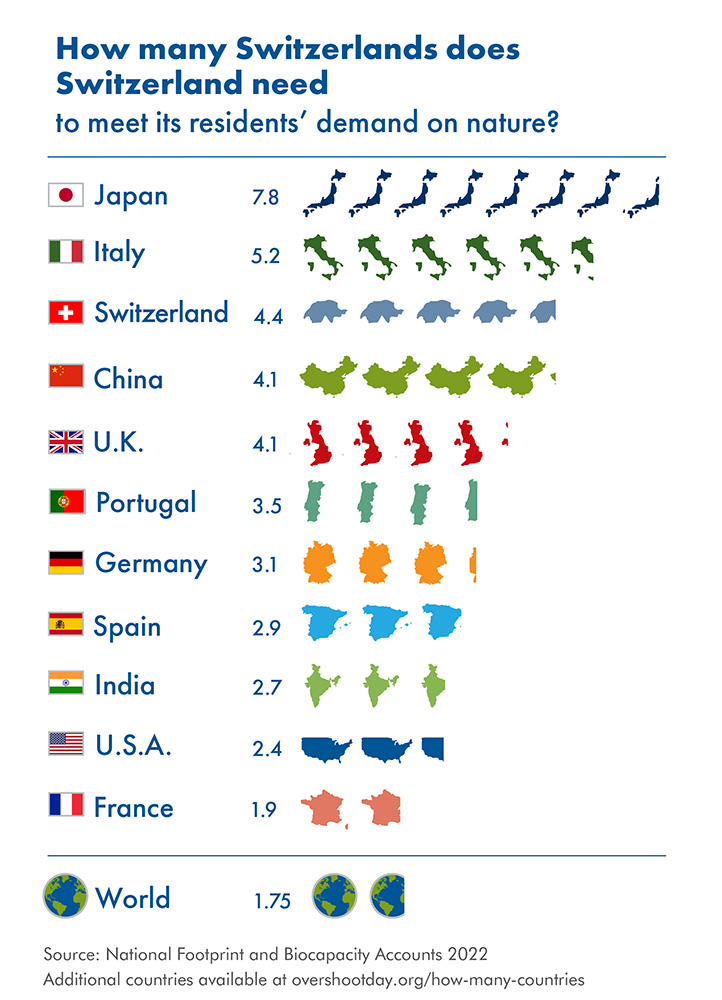
Despite such efforts, as inspiring as they are, Switzerland’s economy is vastly underprepared for the predictable future of climate change and resource constraints. It continues to use over 4 times more than Swiss ecosystems can renew and remains exposed to resource risks.
If Switzerland followed its original Paris goal of cutting its 1990-emission in half by 2030, Swiss Overshoot Day would move by 72 days to July 24th. Yet sadly, sluggish official efforts are undermining Switzerland’s ability to remain successful in the predictable future of climate change and resource constraints. What holds Switzerland back from embracing resource security?
Media Contact
media@footprintnetwork.org
mobile: + 41 78 656 2835
More background
Why overshoot matters for the country’s economy
The future has never been more predictable. We know that people will want to eat and sleep. They also want to be mobile, feel safe, and have fun. In addition, it is evident that we will live in a world with increased climate change and growing resource constraints. This is true in every imaginable scenario. Also, this future is approaching faster than our cities, companies, energy infrastructure, and food systems can adjust.
As a result, resource security is turning into a central indicator of economic strength. The lasting war in Ukraine and the resource disruptions it has caused serve as an illustration. The war has demonstrated our fragile dependence on fossil fuel. Massive efforts have helped us decouple from the Russian supply, but our fossil fuel dependence is still enormous. A rapid energy and resource transition will reward the world with less extreme climate change and the actor with a far more reliable resource situation. Just consider that today, Switzerland consumes 4.4 times more than its own ecosystems can regenerate.
Prolonging our fossil fuel dependence increases the risk of being stuck with less useful (and eventually, stranded) assets, global tensions, and political unrest. Food security becomes particularly critical, with direct implications for Switzerland’s globally integrated economy.
Those who delay their energy and resource transition expose themselves to increasingly large and uneven risks. Inequalities grow between those who prepare wisely and build resilience, and those who wait, weakening themselves. Those who fail to embrace change will fall behind. It is a double risk, as they will be fragile in an increasingly fragile world. “It is unclear whether Switzerland has the resolve to prepare itself adequately for the predictable future of climate change and resource constraints. The war in Ukraine may have been a wake-up call, yet at the same time, the political will to truly shift is still small” said Steven Tebbe, CEO of Global Footprint Network. “While good efforts exist in Switzerland, such as boosting the thermal efficiency of houses or using electricity from hydropower, the country overall is still far from being fit for operating in a world resulting from persistent overshoot. The gap continues to be immense.”
Based on 2018 data, the food consumption of Swiss residents alone required the capacity of more than one entire Switzerland. The same amount was needed to maintain Swiss mobility. 77% of the biological resource requirement of the Swiss comes from abroad.
Housing alone occupies about 1/6th of the entire demand. Given its significant position, we have partnered with Eberhard, a construction company, who is pioneering construction waste recycling. Patrick Eberhard, a company board member, emphasizes that “infrastructure has tremendous lock-in effects. For the better or the worse. Therefore, getting construction right is a big piece of the puzzle.”
Cities, companies, or countries that fail to prepare for the foreseeable future will be largely disadvantaged. Acting fast, while also getting it right, will become increasingly essential as the physical infrastructure of cities and companies are adapting slower than the resource-constrained future is descending upon us. How is Switzerland positioned? What are our options?
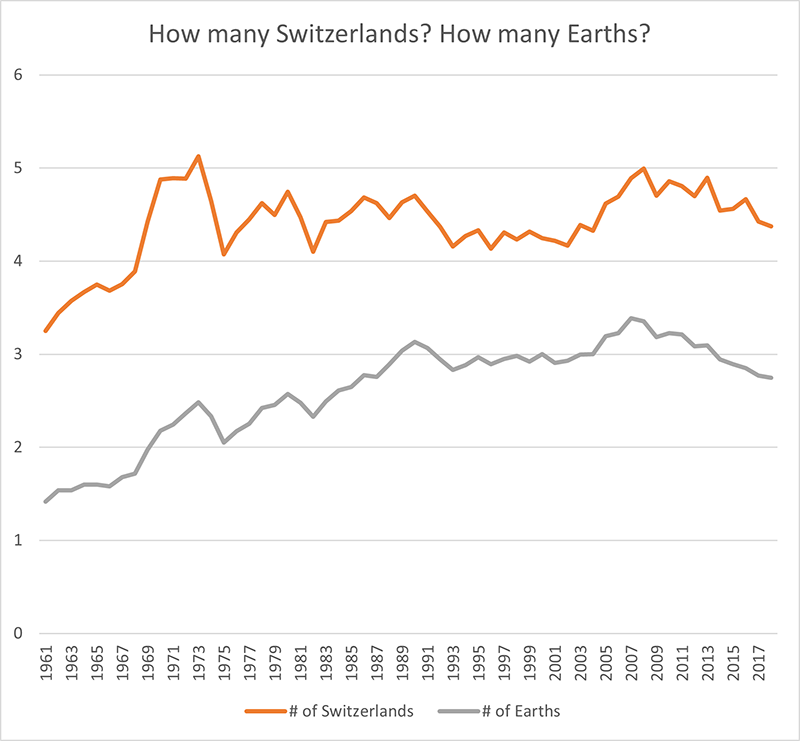
The figure above charts the number of Switzerlands needed to support Switzerland’s resident’s annual resource consumption against the number of Earths needed if all people lived like residents of Switzerland.
One thing is obvious. The speed and scale at which Switzerland is transforming its economy erodes Switzerland’s longer-term prospects.



